How To Reduce Surface Water Run-Off In Your Yard: Effective Strategies
Install rain gardens and permeable pavements to reduce surface water run-off in your yard. Implement proper grading to direct water flow.
Surface water run-off can cause erosion and flooding issues in your yard. Addressing this problem improves your landscaping and prevents potential damage. Rain gardens are effective in absorbing excess water, reducing run-off. Permeable pavements allow water to seep through, preventing pooling and promoting groundwater recharge.
Proper grading ensures water flows away from your home and into designated areas. These methods create a sustainable, eco-friendly yard that handles rain efficiently. By incorporating these solutions, you enhance your yard’s health and resilience.
Rain Gardens
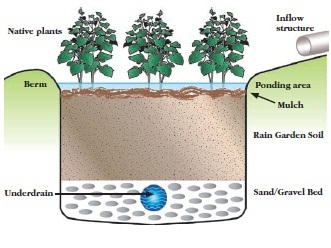
Rain gardens are a simple and beautiful way to reduce surface water run-off in your yard. They help absorb rainwater, filter pollutants, and provide a habitat for wildlife. Plus, they can be a stunning addition to your landscape.
Design Tips
Designing a rain garden requires some planning. Follow these tips for success:
- Location: Choose a low spot in your yard where water naturally pools.
- Size: The garden should be about 20% the size of the area that drains into it.
- Depth: Dig your garden 4-8 inches deep to allow water to collect and absorb.
- Soil: Use a mix of sand, compost, and topsoil for good drainage.
Plant Selection
Selecting the right plants is crucial for a thriving rain garden. Here are some tips:
- Native Plants: Native plants are best because they are adapted to local conditions.
- Water Tolerance: Choose plants that can handle both wet and dry conditions.
- Plant Diversity: Use a mix of grasses, flowers, and shrubs for variety.
| Plant Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Grasses | Blue Fescue, Switchgrass |
| Flowers | Black-Eyed Susan, Purple Coneflower |
| Shrubs | Redosier Dogwood, Winterberry |

Credit: porch.com
Permeable Paving
Permeable paving is a smart solution to reduce surface water run-off in your yard. It allows water to seep through the surface, reducing flooding and erosion. This eco-friendly option supports groundwater recharge and minimizes water pollution.
Material Options
Choosing the right materials for permeable paving is crucial. Here are some popular options:
- Porous Asphalt: Asphalt with tiny holes that let water pass through.
- Permeable Concrete: Concrete mixed to allow water to flow through easily.
- Gravel: Loose stones that provide excellent drainage.
- Permeable Pavers: Interlocking bricks designed with gaps for water infiltration.
Installation Guide
Follow these steps to install permeable paving in your yard:
- Plan: Measure the area and choose your materials.
- Excavate: Dig out the area to a depth of 8-12 inches.
- Base Layer: Add a 4-inch layer of crushed stone.
- Geotextile Fabric: Lay fabric to prevent soil mixing with the gravel.
- Second Layer: Add another 4-inch layer of crushed stone.
- Lay Pavers: Place the permeable pavers on top.
- Fill Gaps: Fill gaps between pavers with small stones or sand.
- Compact: Use a compactor to settle everything in place.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Plan | Measure area and choose materials |
| Excavate | Dig out 8-12 inches of soil |
| Base Layer | Add 4 inches of crushed stone |
| Geotextile Fabric | Lay fabric to prevent soil mixing |
| Second Layer | Add another 4 inches of crushed stone |
| Lay Pavers | Place permeable pavers on top |
| Fill Gaps | Fill gaps with small stones or sand |
| Compact | Use a compactor to settle everything |
Green Roofs
Green roofs are an innovative way to manage surface water run-off. They offer many benefits to your yard and the environment.
Benefits
Green roofs provide several significant benefits:
- Water Absorption: They absorb rainwater, reducing run-off.
- Temperature Regulation: They help in cooling your home.
- Air Quality Improvement: Plants filter pollutants from the air.
- Wildlife Habitat: Green roofs support local wildlife.
Maintenance Tips
Maintaining a green roof is crucial for its effectiveness:
- Regular Watering: Water the plants during dry periods.
- Weeding: Remove weeds that can harm the plants.
- Fertilization: Use organic fertilizers to nourish the plants.
- Inspection: Check for any leaks or damage.
These steps will help you keep your green roof healthy and functional.
| Task | Frequency |
|---|---|
| Watering | Weekly |
| Weeding | Monthly |
| Fertilization | Seasonally |
| Inspection | Quarterly |

Credit: www.lawnstarter.com
Swales And Berms
Swales and berms are excellent solutions to reduce surface water run-off in your yard. These structures can help you manage water flow, preventing erosion and improving soil health. Swales are shallow ditches that capture and direct water. Berms are raised areas that help control the flow of water. Together, they create an effective system for water management in your yard.
Construction Steps
- Plan the Layout: Determine the best location for your swale and berm. Use a level to identify the natural slope of your yard.
- Mark the Area: Use stakes and string to outline the swale and berm. Ensure the swale runs perpendicular to the slope.
- Excavate the Swale: Dig a shallow trench along the marked line. The depth should be about 6-12 inches.
- Build the Berm: Use the soil from the swale to create the berm. Place it on the downhill side of the swale.
- Shape and Compact: Shape the berm and swale for smooth water flow. Compact the soil to prevent erosion.
- Plant Vegetation: Plant grasses and shrubs on the berm and swale. This helps stabilize the soil and absorb water.
Best Practices
- Choose Native Plants: Native plants are more adapted to local conditions. They require less maintenance and water.
- Maintain Your Swale and Berm: Regularly check for signs of erosion or blockages. Clear debris to ensure proper water flow.
- Use Mulch: Apply mulch around plants to retain moisture and reduce erosion.
- Consider Adding Rocks: Place rocks in the swale to slow down water flow. This reduces the risk of erosion.
- Adjust as Needed: Monitor the system during heavy rains. Make adjustments to improve water management.
Dry Wells
Reducing surface water run-off is essential for a healthy yard. One effective solution is using dry wells. They help manage excess water, preventing flooding and erosion.
How They Work
A dry well is an underground structure. It collects and disperses water. Water is redirected from gutters or low spots. The dry well allows water to seep into the ground. It helps recharge groundwater and prevents puddles.
Installation Process
- Choose a Location: Pick a spot away from your home. Ensure it’s far from foundations and septic systems.
- Dig a Hole: The hole should be deep and wide. A typical size is 3 feet in diameter and depth.
- Prepare the Base: Add gravel to the bottom of the hole. This helps with drainage.
- Place the Dry Well: Insert the dry well into the hole. Ensure it is level.
- Connect Drain Pipes: Attach pipes from downspouts or low areas. Ensure a snug fit to prevent leaks.
- Backfill with Gravel: Fill around the dry well with gravel. This allows water to flow freely.
- Cover with Soil: Add soil over the gravel. Plant grass or other vegetation to blend with your yard.
Using dry wells is an effective way to manage surface water run-off. It helps keep your yard dry and healthy.
Native Plants
Native plants are an excellent choice for reducing surface water run-off in your yard. These plants are well-adapted to the local environment and require less maintenance. They also support the local ecosystem and promote biodiversity.
Advantages
Using native plants in your yard has many advantages:
- Water efficiency: Native plants need less watering.
- Soil stabilization: Their deep roots help hold soil in place.
- Habitat creation: They provide shelter for local wildlife.
- Less maintenance: Native plants are adapted to local conditions.
- Pollution reduction: They require fewer fertilizers and pesticides.
Choosing Species
When choosing native plants, consider the following factors:
| Factor | Details |
|---|---|
| Climate | Choose plants that thrive in your local climate. |
| Soil Type | Consider the soil type in your yard. |
| Sunlight | Ensure the plants match the sun exposure in your yard. |
| Water Needs | Choose plants with low water needs to reduce run-off. |
Here are some tips for selecting native species:
- Consult with local nurseries or botanical gardens.
- Check local environmental groups for advice.
- Research online databases for native plants in your area.
Some popular native plants include:
- Milkweed – attracts butterflies.
- Black-eyed Susan – bright yellow flowers.
- Blue Lupine – adds vibrant blue color.
Rain Barrels
Rain barrels are an excellent way to reduce surface water run-off. They collect and store rainwater from your roof. This stored water can be used for many purposes. Using rain barrels helps the environment and saves money on your water bill.
Setup Instructions
Setting up a rain barrel is simple and quick. Follow these steps:
- Choose a location: Place the barrel under a downspout.
- Prepare the area: Ensure the ground is level.
- Install the barrel: Cut the downspout and attach it to the barrel.
- Secure the barrel: Use a sturdy base to keep it stable.
- Connect overflow: Attach a hose to direct extra water away.
Usage Ideas
There are many ways to use the water collected in rain barrels:
- Garden irrigation: Use the water for your plants and flowers.
- Car washing: Save tap water by using rainwater.
- Cleaning: Clean outdoor furniture and tools with rainwater.
- Pond filling: Fill your garden pond with rainwater.
| Advantages | Details |
|---|---|
| Water Conservation | Saves tap water by using rainwater. |
| Cost Savings | Reduces water bills. |
| Environmental Impact | Decreases stormwater run-off. |
Credit: www.fairfaxcounty.gov
Mulching
Mulching is a powerful technique for reducing surface water run-off in your yard. It helps retain soil moisture, prevent erosion, and improve soil health. By covering the soil with a protective layer, mulch slows down water, allowing it to seep into the ground.
Types Of Mulch
There are several types of mulch you can use in your yard:
- Organic Mulch: Includes wood chips, straw, and compost. It decomposes over time, enriching the soil.
- Inorganic Mulch: Includes gravel, stones, and plastic sheeting. It does not decompose and lasts longer.
- Living Mulch: Includes ground cover plants. It provides a natural look and helps control weeds.
| Type of Mulch | Benefits | Drawbacks |
|---|---|---|
| Organic Mulch | Improves soil health | Needs to be replaced regularly |
| Inorganic Mulch | Long-lasting | Does not improve soil |
| Living Mulch | Natural look | Requires maintenance |
Application Techniques
Applying mulch correctly ensures maximum benefit:
- Prepare the Area: Remove weeds and debris from the soil surface.
- Layer Thickness: Spread mulch 2-4 inches thick. Too thick can suffocate plants.
- Keep Away from Stems: Avoid piling mulch against plant stems to prevent rot.
- Water Before Mulching: Water the soil before applying mulch to help it settle.
Mulching is an easy and effective way to manage water run-off. Choose the right mulch type and apply it correctly for best results.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Surface Water Run-off?
Surface water run-off occurs when rainwater flows over the yard instead of seeping into the soil.
How Can I Reduce Yard Run-off?
Install rain gardens, use permeable paving, and add mulch to absorb water and reduce run-off.
Why Is Reducing Water Run-off Important?
Reducing water run-off prevents soil erosion, reduces flood risk, and improves water quality in nearby water bodies.
Conclusion
Implementing strategies to reduce surface water run-off can transform your yard. Use rain gardens, permeable pavers, and native plants. These methods help manage water efficiently and protect the environment. Start small, make consistent efforts, and enjoy a healthier yard. Your actions today will benefit future generations and enhance your outdoor space.







